Location Services
ENWLSI Notes from CAP 13 - Location Services Deployment
- Cisco Mobility Service Engine (MSE) + Cisco Mobile Experience (CMX)
- Cisco DNA Spaces
Indoor Location Protocols
Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) is a part of IEEE 802.15.4 and transmits pulses in a wide bandwidth spectrum of 500 MHz. The protocol is not widely used and Cisco does not support it yet.
UWB is useful for real-time location systems, and its precision capabilities and low power make it well-suited for radio-frequency-sensitive environments, such as hospitals. UWB is also useful for peer-to-peer fine ranging, which allows many applications based on relative distance between two entities.
The frames are marked with a timestamp and a time of flight (ToF) is calculated to estimate the range between client and access point.
Bluetooth Low Energy BLE (version 4.0 made in 2010) uses connectionless message to exchange Tx power information and triangulate the positions of other BLE objects.
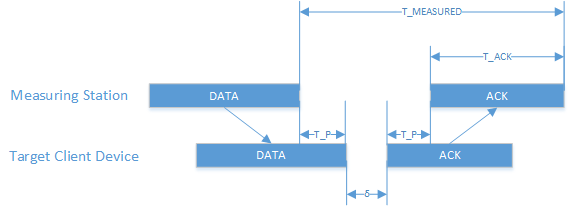
Wi-Fi from 2012 to 2016 includes FTM (fine timing measurements) in the initiating station messages (ISTA) to calculate the distance using ToF. FTM is a feature included in the 802.11mc that is a maintenance revision of the 802.11 WLAN standards like: 802.11ae, aa, ad, ad and af.
802.11-based location techniques
Cell of Origin is used only for presence detection. With the RSSI information of a wireless client from 3 or more access points we can triangulate the position using RSSI Trilateration. This method is affected by enviroment attenuation and client transmit power unknown to the access point. This technique checks management broadcast frames.
The AP must receive 802.11 frames to estimate the signal strength or angle. The ap listen on one channel at time so in a group of AP, correctly configured with different adjacent channels, just one ap is able to determine the presence of the client.
The location of a client must be paired with an identity so the type of frames is critical:
- Frame timing: broadcast management frames timing like 5 to 6 minutes interval of probing
- MAC hiding: broadcast and discovery frames have randomized
- Associated client send frequent, high data rates unicast frames that are demodulated by only the AP to which the station is associated and only one AP not provide great location results. Adding unicast frames with a stable MAC address to broadcast frames enhance the precision, this process is called Cisco FastLocate (source).
- Cisco’s Hyperlocation calculates the position of the client evaluating the Angle of Arrival (AoA) using the client signal reaching the 16 to 32 mini directional antennas. So the client position is estimated with just one access point. This method uses any OFDM frames both broadcast and unicast and it is the most accurate with a refresh rate from 2 to 4 seconds and 1 to 3 meters of precision.


Deploying location services
These are the actors behind location services
- The ap collect information from the client
- The WLC does not know the AP mapping so it collects information like detecting AP, detection time, RSSI, AoA and, grouped by MAC address, send them to CMX, MSE or DNA Spaces.
- Fast Locate and AoA can be sent through the WLC (which is transparent towards this data) to the location engine using Network Mobility Service Protocol
Location Engine and Services: CMX/MSE, Connector and DNA Spaces
MSE is the appliance an CMX is the software package that runs on MSE. MSE is typically on premise and can be virtualized. DNA Spaces, which is July System bought from Cisco in 2018, is a cloud based location engine. 9800 WLC and new AireOS release work out of the box, older WLC need a DNA Space relay colled Connector.
Services
- See license offers business metrics, Wi-Fi metrics, real-time metrics, location computation (RSSI trilateration), and location hierarchy visualization.
- Act license offers all the features available in the See license and also the Captive portal function (what MSE calls “Connect”) with profile rules and Engage features (to send notifications to Wi-Fi users based on rules and the user location), an API to expose location to third-party applications (with Webhook), a partner stream feature (to stream data in and out of DNA Spaces), operational insights, and Hyperlocation if you also have an on-premises CMX (where this Hyperlocation is first computed).
- Analytics based on data from Detect and Locate: visit number, distribution, frequency and duration. Visitors path and dwell time (stationary time in a zone).
- Location-based guest portals
- Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) on MSE
Key terms
- DNA Spaces
- MSE
- CMX
- RSSI Trilateration
- Hyperlocation
- location precision
- location accuracy
