Git
From Wikipedia - The source code for Git refers to the program as “the information manager from hell”. (in fact, “Git tzu Gehinom” means “go to hell” in Yiddish).
Summary
Summarizing old collections of notes to track the logic behind code versioning in general and git. Not a trustful guide.
Links
.gitconfig
Work in progress..
Actions
Coding > Adding code > Code is in STAGING AREA > Commit code > Push to GitHub
Remember that the HEAD is the pointer.
-
git init -
git status -
git add .orgit add main.py -
git log: commit ID, author, dategit log --oneline: lookup the hash ID
Commit
git commit -m "message" -m "additional notes"atomic changes- You can’t switch branches without commits
- Check the stashing of files
git restore: undo a commit
git commit -am "messagegit commit --amend -m "git notes, pull codechange the name of the last commit message
Each commits are linked to the previous commit. Check HEAD to show where the code is pointing.
git config --global: user.name, user.email
Reverting a commit (come tornare indietro di commit)
git revert HEADannull the last commitgit revert <commit_hash>annull a specific commit generates a new commit by default safer for remote branches
Resetting a commit (come tornare indietro di commit)
less safe for shared branches than revert
git reset --soft HEAD~1removes the last commit but keeps the changes staged (in the index).git reset --mixed HEAD~1removes the last commit and unstages the changes, but keeps them in the working directory. This is the default behavior if you omit the option.git reset --hard HEAD~1Removes the last commit and discards all changes in the working directory and staging area. ⚠️ This is destructive—use with caution!
Branching
git branch branch-name: creating new branchgit switch -c branch-name: build a branch and move to itgit checkout -d branch-name: build a branch and move to it
git checkout dev-branchorgit switchYou can move stashed code between branches, checkgit stashgit branch -M newname: renaming branch
Checkout
git checkout [ hash ]: move between commits (use hash id) or branches- Moving back to the previous commit using
git reflogorgit checkout branch-name git log --onelineto check the hash
Merging dev files to main
git checkout main: not only used for merging, you can move between commits with checkoutgit merge devgit branch -d dev: Deleting the branch- After branching is usual to do a
commit
Diff
git diff: diff between staged and unstaged of the same files or between commits or between branch of the same file- you need to read plus and minus symbols with the direction of files in mind
- not alway plus means adding code
git diff --staged: diff staged and unstaged filesgit diff [commitid] [commitid]orgit diff [commitid]..[commitid]: diff between commits
Stashing
-
git stash: temporary way to save changesgit stash pop: bring up stashed codegit stash listgit stash apply: to apply a specific stash, use stash list to see the id
-
git restore: go back of a commit to undo the current changes
Rebase
Powerful merge tool. Be aware. git rebase takes the branch and attach it to the last commit of the base branch.
main ---- M1 ---- M2 ---- M3
\____ bugfix ____ B1
After rebase
main ---- M1 ---- M2 ---- M3 ---- B1
Only use it from the side branch like a bug fix. After you checkout in side branch then you can go with: git rebase master
Remote repository
-
git remote- Shows configured remotes. -
git remote -v- Shows remotes with their respective URLs. -
git remote add <name> <url>- Adds a new remote.originname of remote repository
-
git remote rename <old> <new>- Renames a remote. -
git remote remove <name>- Removes a remote. -
git remote set-url <name> <new-url>- Changes the URL of a remote. -
git remote show <name>- Details about a remote. -
git remote prune <name>- Removes obsolete references. -
git remote update- Updates all configured remotes.
Pushing code
git push -u origin main- pushing a branch to the remote branch origin saving origin as a upstream of main.git push origin main- without the-uyou are not setting the upstream branch and the next push will failgit push --set-upstream origin main
Pull code
git pull: download code and informationgit fetch: download only information
Hooks folder
Managing action triggers before after push or commit ecc.
Workflow
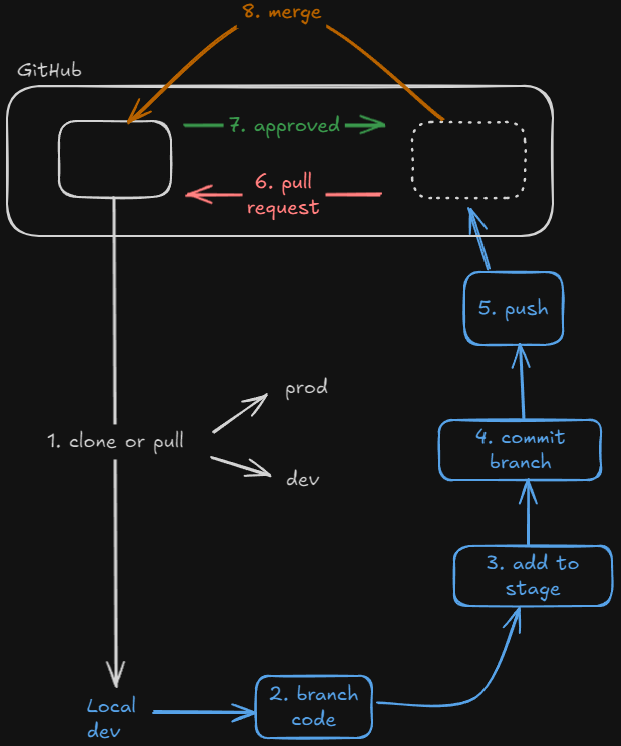
Github Actions
- on push
- live testing on github servers or locally
GitOps
The creation of servers both in the cloud or on premise, is pushed via Terraform or Ansible configurations
- manifests
- playbooks
The previous workflow is applied to these configurations therefore they are testes, rewied before the get applied in any environment.
There are two types of deployment
Push: pushing from the pipeline to the deployment servers Pull: pulling from the agent installed into the deployment servers to the repository
- desired state
- actual state
Flux and Argo
DevOps flow

